Deletion of S. Typhi tolc affects bacterial growth, efflux, adhesion


PDF) Deletion of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi tolC reduces bacterial adhesion and invasion toward host cells

Lack of AcrB Efflux Function Confers Loss of Virulence on Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium

The AcrAB–TolC efflux system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium plays a role in pathogenesis - Buckley - 2006 - Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

Fast bacterial growth reduces antibiotic accumulation and efficacy

Accumulation of H33342 and efflux of ethidium bromide in S. Typhimurium

Genetic Determinants of Salmonella Resistance to the Biofilm-Inhibitory Effects of a Synthetic 4-Oxazolidinone Analog
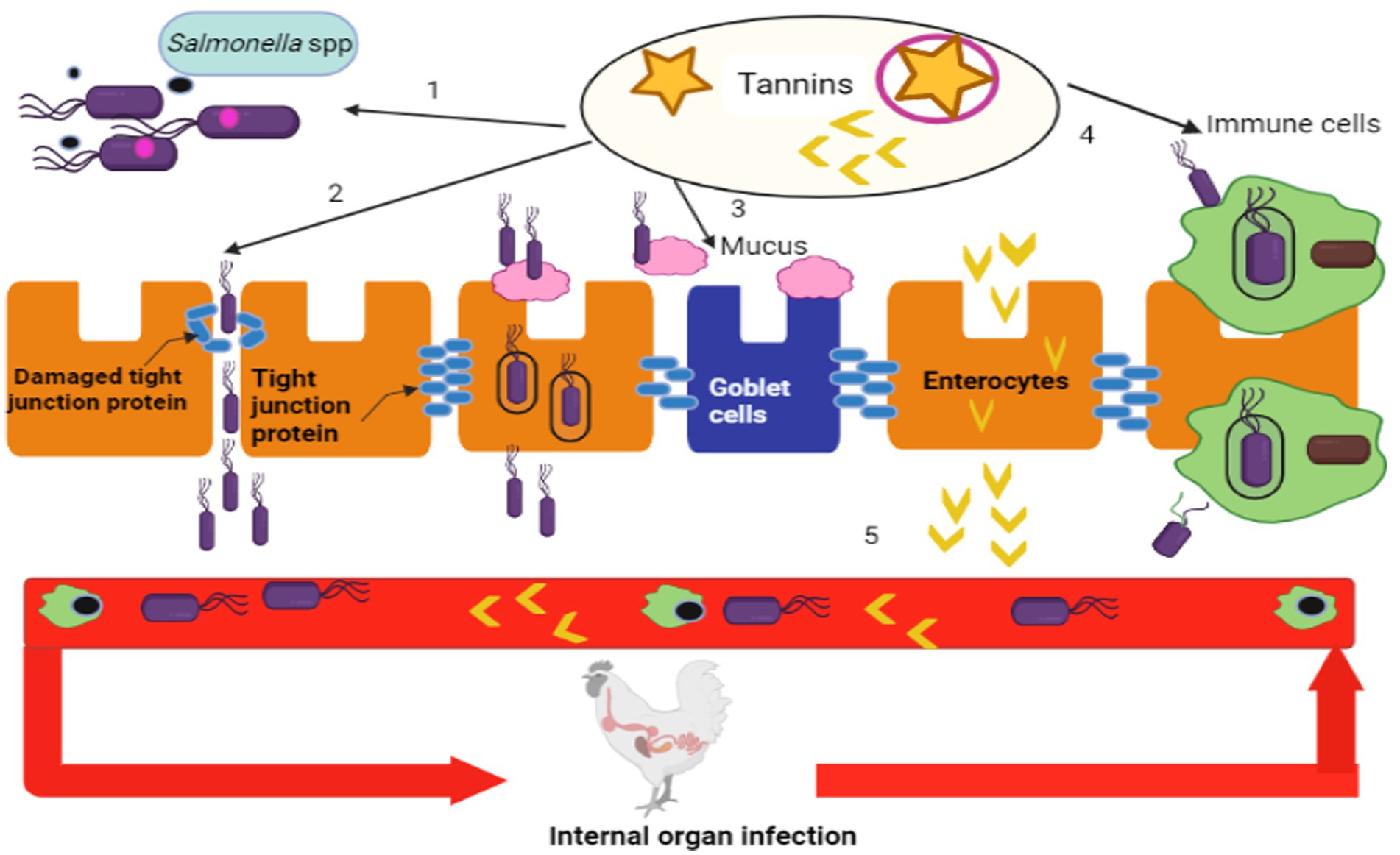
Frontiers Phytochemicals: potential alternative strategy to fight Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
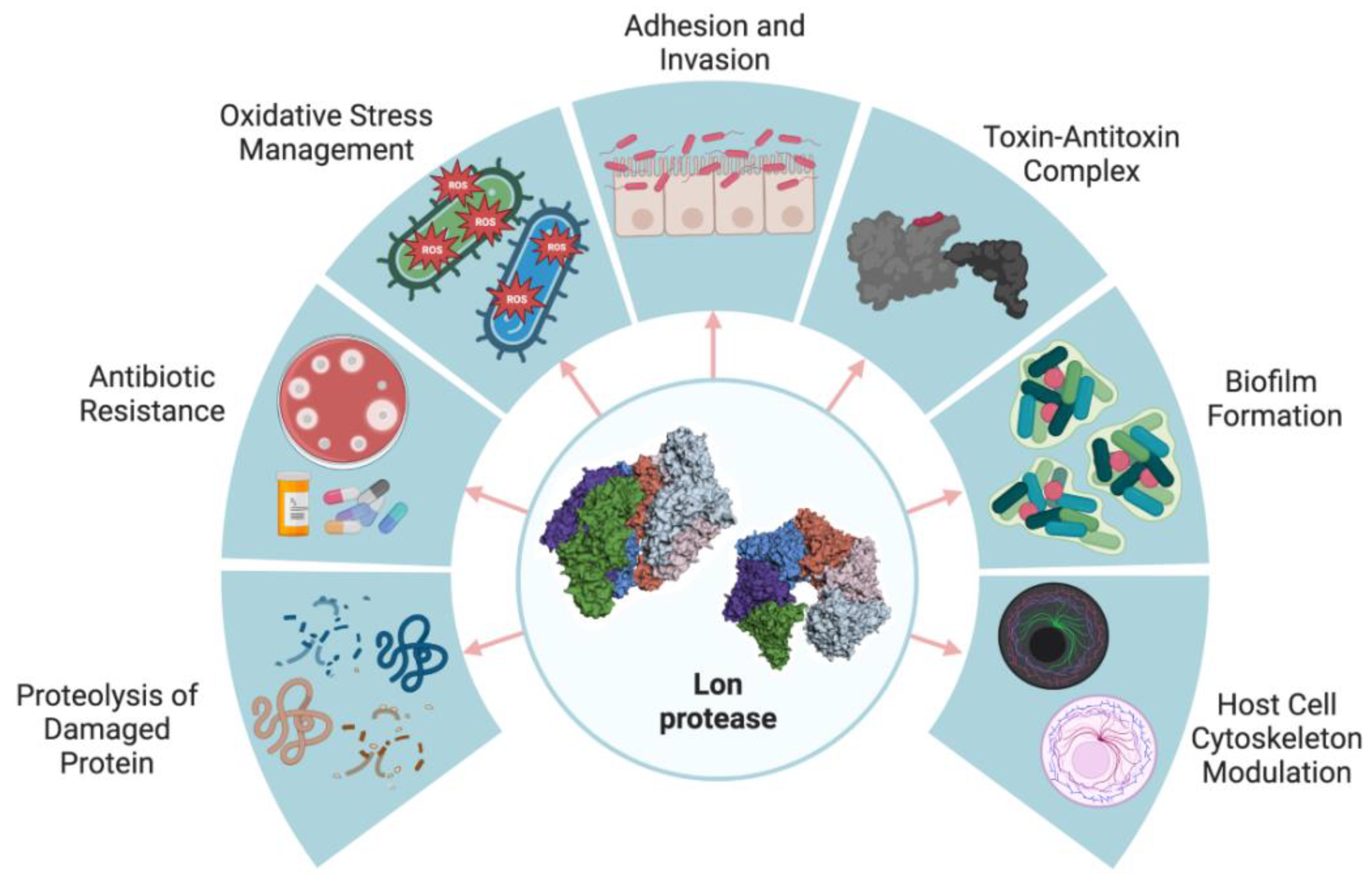
IJMS, Free Full-Text
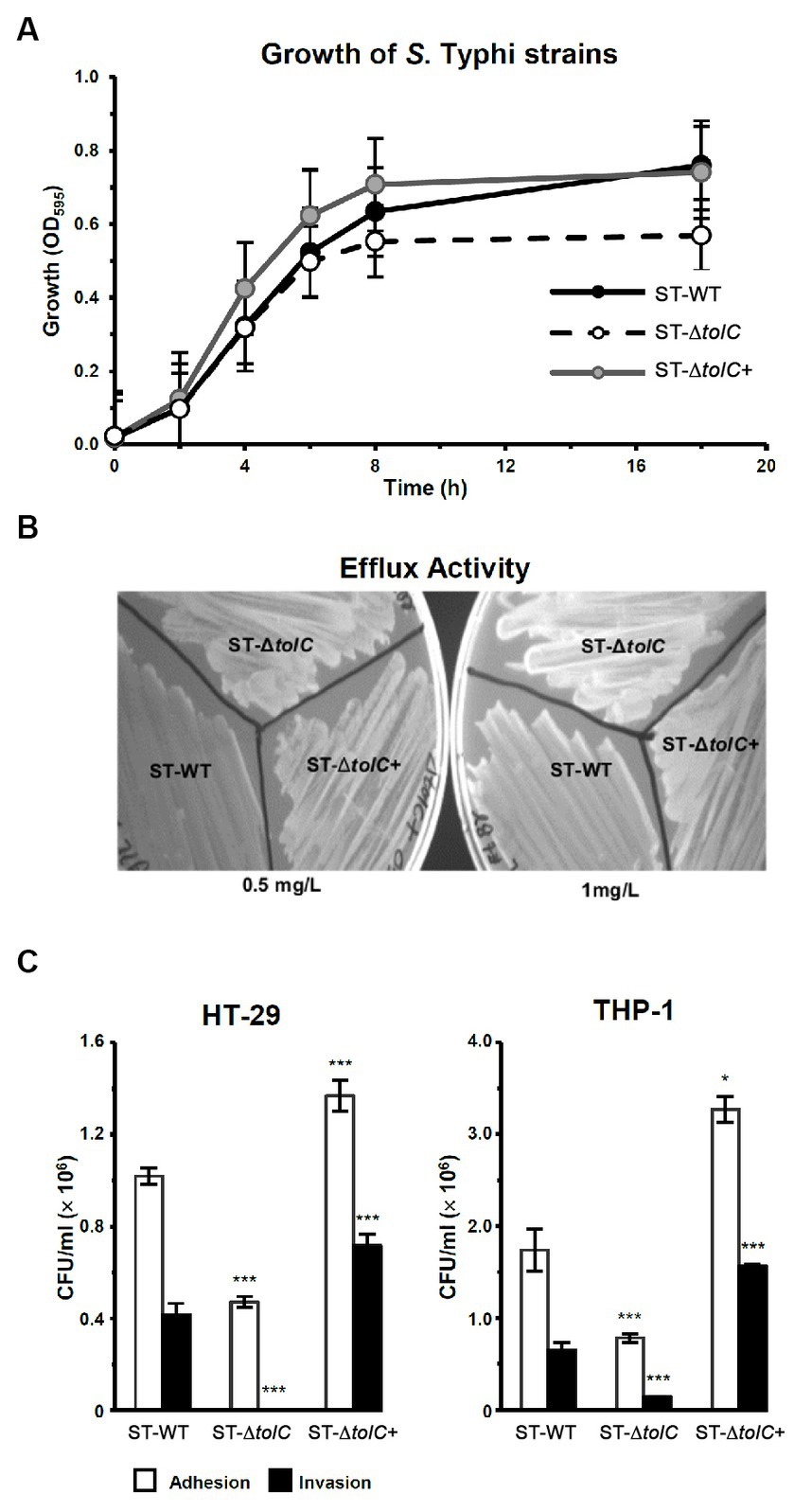
Frontiers Deletion of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi tolC reduces bacterial adhesion and invasion toward host cells
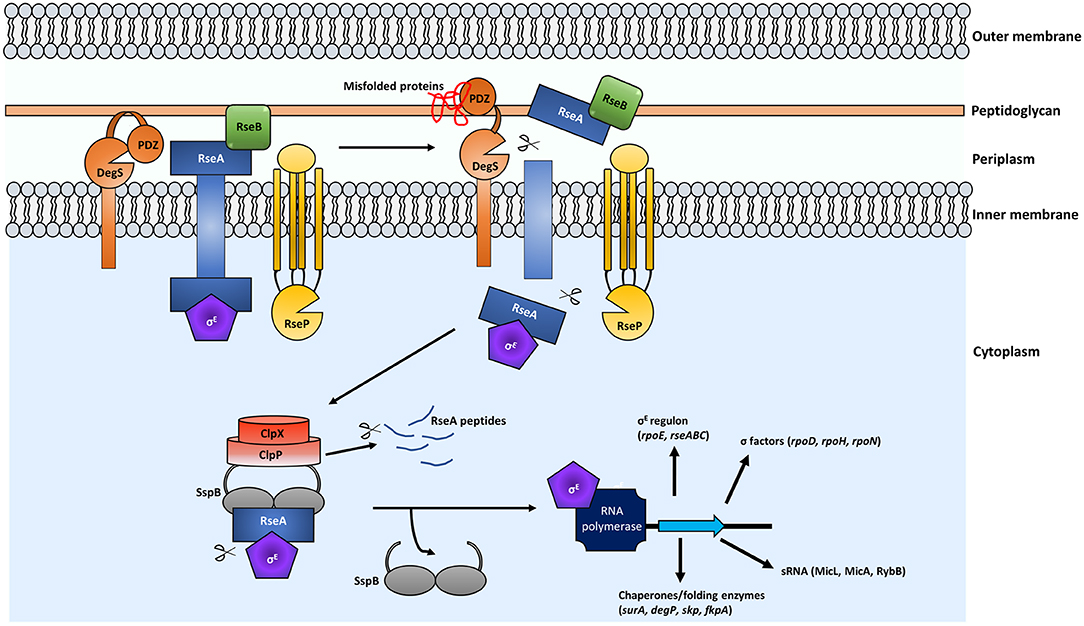
Frontiers Maintaining Integrity Under Stress: Envelope Stress Response Regulation of Pathogenesis in Gram-Negative Bacteria

Physiological Functions of Bacterial “Multidrug” Efflux Pumps

Structure, Assembly, and Function of Tripartite Efflux and Type 1 Secretion Systems in Gram-Negative Bacteria