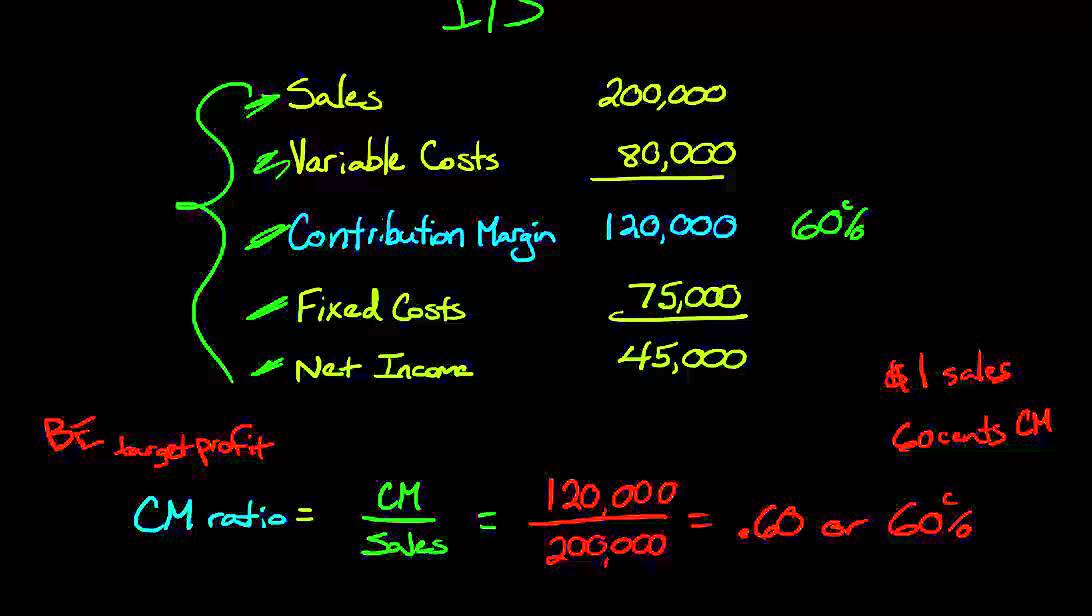
Contribution margin ratio is a calculation of how much revenue your business generates from selling its products or services, once the variable costs involved in producing and delivering them are paid. This can be a valuable tool for understanding how to price your products to ensure your business can pay its fixed costs, such as salaries and office rent, and still generate a profit. The contribution margin ratio is the difference between a company’s sales and variable costs, expressed as a percentage. This ratio shows the amount of money available to cover fixed costs. It is good to have a high contribution margin ratio, as the higher the ratio, the more money per product sold is available to cover all the other expenses.
Contribution Margin Ratio: Definition
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
Ask Any Financial Question
Furthermore, a higher contribution margin ratio means higher profits. This means that $15 is the remaining profit that you can use to cover the fixed cost of manufacturing umbrellas. Also, you can use the contribution per unit formula to determine the selling price of each umbrella. Contribution margin is used to plan the overall cost and selling price for your products. Further, it also helps in determining profit generated through selling your products. Yes, the Contribution Margin Ratio is a useful measure of profitability as it indicates how much each sale contributes to covering fixed costs and producing profits.
- This ratio shows the amount of money available to cover fixed costs.
- If the fixed costs have also been paid, the remaining revenue is profit.
- For example, assume that the students are going to lease vans from their university’s motor pool to drive to their conference.
- The best contribution margin is 100%, so the closer the contribution margin is to 100%, the better.
Contribution Margin Ratio: Definition, Formula, and Example
Instead, management uses this calculation to help improve internal procedures in the production process. Similarly, we can then calculate the variable cost per unit by dividing the total variable costs by the number of products sold. You can calculate the contribution margin by subtracting the direct variable costs from the sales revenue. The difference between the selling price and variable cost is a contribution, which may also be known as gross margin. It’s important to note that contribution margin is different from gross margin.
We’ll start with a simplified profit and loss statement for Company A. The profitability of our company likely benefited from the increased contribution margin per product, as the contribution margin per dollar increased from $0.60 to $0.68. Next, the CM ratio can be calculated by dividing the amount from the prior step by the price per unit. The contribution margin ratio is calculated as (Revenue – Variable Costs) / Revenue. Very low or negative contribution margin values indicate economically nonviable products whose manufacturing and sales eat up a large portion of the revenues.
However, these fixed costs become a smaller percentage of each unit’s cost as the number of units sold increases. The contribution margin is affected by the variable costs of producing a product and the product’s selling price. Yes, it means there is more money left over after paying variable costs for paying fixed costs and eventually contributing to profits. It means there’s more money for covering fixed costs and contributing to profit. Now, add up all the variable costs directly involved in producing the cupcakes (flour, butter, eggs, sugar, milk, etc).
If the contribution margin for an ink pen is higher than that of a ball pen, the former will be given production preference owing to its higher profitability potential. Say a machine for manufacturing ink pens comes at a cost of $10,000. The contribution margin (CM) is the amount of revenue in excess of variable costs. You can even calculate the contribution margin ratio, which expresses the contribution margin as a percentage of your revenue. A firm’s ability to make profits is also revealed by the P/V ratio. With a high contribution margin ratio, a firm makes greater profits when sales increase and more losses when sales decrease compared to a firm with a low ratio.

Recall that Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting explained the characteristics of fixed and variable costs and introduced the basics of cost behavior. Let’s now apply these behaviors to the concept of contribution margin. The company will use this “margin” to cover fixed expenses and hopefully to provide a profit.
Now, let’s try to understand the contribution margin per unit with the help of an example. Variable Costs depend on the amount of production that your business generates. Accordingly, xero accounting community these costs increase with the increase in the level of your production and vice-versa. This means the higher the contribution, the more is the increase in profit or reduction of loss.
The higher your company’s ratio result, the more money it has available to cover the company’s fixed costs or overhead. A contribution margin analysis can be done for an entire company, single departments, a product line, or even a single unit by following a simple formula. The contribution margin can be presented in dollars or as a percentage.
